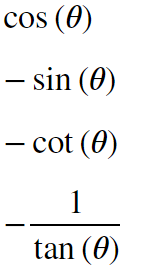SymPyモジュールを使うと、数値だけでなく代数的にも三角関数の演算をすることができます。使いようによってはとてつもないことができそうです。
負角の計算(Negative angles)
まずは、小手調べに負角からです。
display(sympy.sin(-theta))
display(sympy.cos(-theta))
display(sympy.tan(-theta))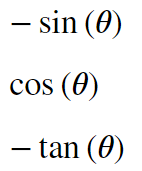
sinはマイナスになります。「サインは出る、コスると消える」というやつで、tanはsin/cosで計算できます。
補角(supplementary angle)
180度($\pi$)との差の計算です。面倒くさいのでsympy.piを変数piに代入し、今後はこの変数を使います。
pi=sympy.pi
display(sympy.sin(pi-theta))
display(sympy.cos(pi-theta))
display(sympy.tan(pi-theta))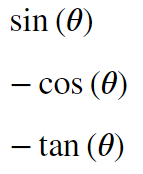
余角(complementary angle)
余角の場合はsinとcosが入れ替わります。
display(sympy.sin(pi/2-theta))
display(sympy.cos(pi/2-theta))
display(sympy.tan(pi/2-theta))
display(sympy.tan(pi/2-theta).rewrite(sympy.tan(theta)))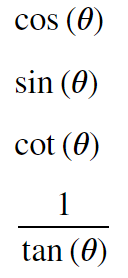
したがってtanの場合は逆数になって、cotで表示されます。tanを使いたい場合はrewriteメソッドを使います。
$\pi$を足す場合
同様に次のように計算することができます。
display(sympy.sin(pi+theta))
display(sympy.cos(pi+theta))
display(sympy.tan(pi+theta))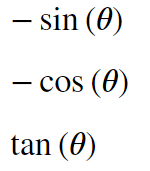
$\pi/2$を足す場合
sinとcosが入れ替わるので、tanの場合にはrewriteメソッドを使います。
pi=sympy.pi
display(sympy.sin(pi/2+theta))
display(sympy.cos(pi/2+theta))
display(sympy.tan(pi/2+theta))
display(sympy.tan(pi/2+theta).rewrite(sympy.tan(theta)))